Introduction
one of the important concepts of topologies in computer networking because you can not manage anything if you don’t have the structured way of managing so topology is nothing but the way of managing interconnected node or computers.
The topology of a network is defined as the geometric representation of the relationship of all the Edges and nodes.
Types of topologies in computer network
1. Star topology
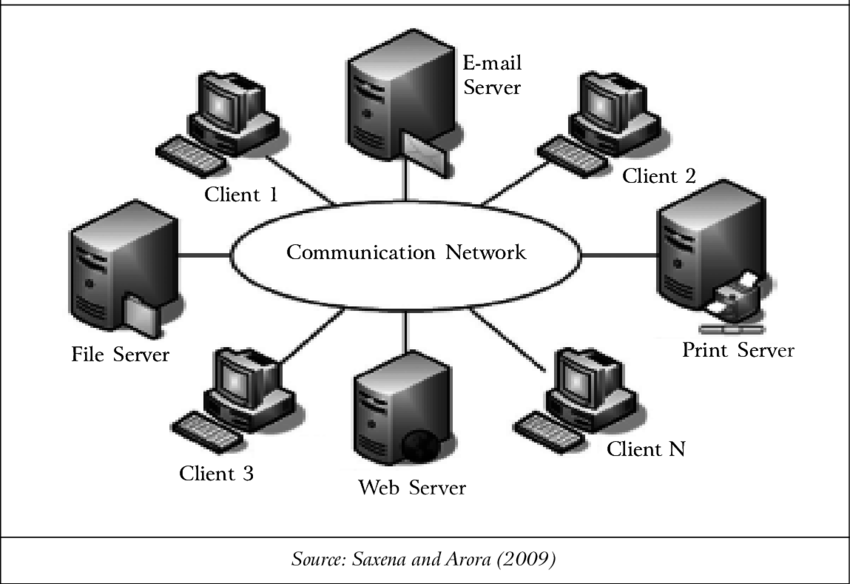
In star topology each device has a dedicated point-to-point link on it to a central controller, usually called hub or switch. The devices are not directly connected to one another.
Each computer on a star network first communicates with a central hub/switch that forwards the message either to all the computers or only to the destination computers.
2. Bus topology
In bus topology, all nodes are connected to a central cable which is called a bus. This bus is also called Trunk or sometimes it was also referred to as Backbone cable. • Trunk cable was then connected to the branch cables which were further connected to the PCs. Every network device communicates with the other device through this Bus.
When one computer sends a signal up the wire, all the computers on the network receive the information, but only one accepts the information
3. Ring topology
In ring topology, the computers in the network are connected in a circular fashion which form of a ring. In ring topology, each computer is connected to the next computer, with the last one connected to the first or we can say each device is connected to other two devices with a dedicated link in one direction, from device to device. Each computer in the ring incorporates a repeater.
4. Mesh topology
In a mesh network topology, each of the network nodes, computer and other devices, are interconnected with one another with dedicated point to point link.
5. Tree topology
As its name implies in this topology devices make a tree structure. It is also called a hierarchical topology. Tree topology integrates the characteristics of star and bus topology. In tree topology, the numbers of star networks are connected using Bus. This main cable seems like a main stem of a tree, and other star networks as the branches.
Read more : what is networking ?
6.Hybrid topology
Hybrid, as the name suggests, is a mixture of two different things. A hybrid topology is a combination of two or more network topologies. The topology that combines more than one topology is called hybrid topology. Two common examples for hybrid networks are star ring network and star bus network
1. A star-ring network consists of two or more star topologies connected using a Multistation Access Unit (MAU) as a centralized hub.
2. A star-bus network consists of two or more star topologies connected using a bus trunk (the bus trunk serves as the network’s backbone).
First use of topologies in history
The bus topology was one of the earliest network designs used in computer networks, particularly during the 1960s and 1970s. It was notably implemented in ARPANET, the precursor to the modern internet. In this topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable, known as the bus. This simple and cost-effective design allowed for easy expansion and minimal cabling. However, it had limitations such as limited scalability, a single point of failure, and challenging troubleshooting. Despite these drawbacks, the bus topology played a crucial role in the early development of computer networks, laying the foundation for more advanced network designs
Conclusion
In summary, network topology is a fundamental concept in computer networking that defines the arrangement and interconnection of various devices within a network. Understanding different topologies, such as bus, star, ring, mesh, and hybrid, is crucial for designing efficient and reliable networks. Each topology has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to choose the right one based on the specific needs and goals of the network. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of robust and well-designed network topologies will only grow, ensuring seamless communication and data exchange in our increasingly connected world.